Blackened Tooth near the Gum Line: Why Do Teeth Darken

Contents:
Cervical caries differs from other forms of caries process by the decay-deepening rate. This is due to the natural thinness of the enamel layer in the cervical area. Modern treatment methods make it possible to achieve good aesthetic results even in challenging clinical cases. However, lack of professional care quickly leads to tooth decay and premature loss. Another complication is chronic periodontitis, which requires complex and long-term therapy. Do not delay treatment.
Tooth enamel darkening at the root or cervical caries is a pathological process localized in the gingival area of the tooth cervix. The main symptoms are enamel softening and darkening, sensitivity to food or temperature stimuli, and pain. Cervical caries can occur on all teeth and develop at any age. Experts at the Clinic of Aesthetic Dentistry consider this localization of dental caries to be the most dangerous since the decay occurs in the most vulnerable spots and quickly leads to the destruction of the crown. Dental fillings today quickly solve the problem of tooth decay. Do not delay going to the doctor – start your treatment today.
Why Do Teeth Darken: Key Factors
The cervical dental caries development mechanisms do not differ from those of any other localized dental lesion. However, several factors can contribute to the risk of developing cavities in the cervical zone:
- tooth erosion;
- pathological bite;
- wrong brushing technique;
- periodontitis;
- tartar, plaque;
- excessive use of whitening toothpaste, at-home whitening products (lemon, activated charcoal, baking soda, etc.);
- specific diseases: diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases.
There is a direct link between the teeth turning black and gingivitis. However, it is also essential to take into account some anatomical features. For example, the enamel thickness in the neck area is only 0.1 mm, while in the middle of the incisor, it reaches 1.5-1.7 mm, and in the fissure area, it is 0.6-0.7 mm.
Live Tooth Is Turning Dark: What Does Tartar Have to Do with It?
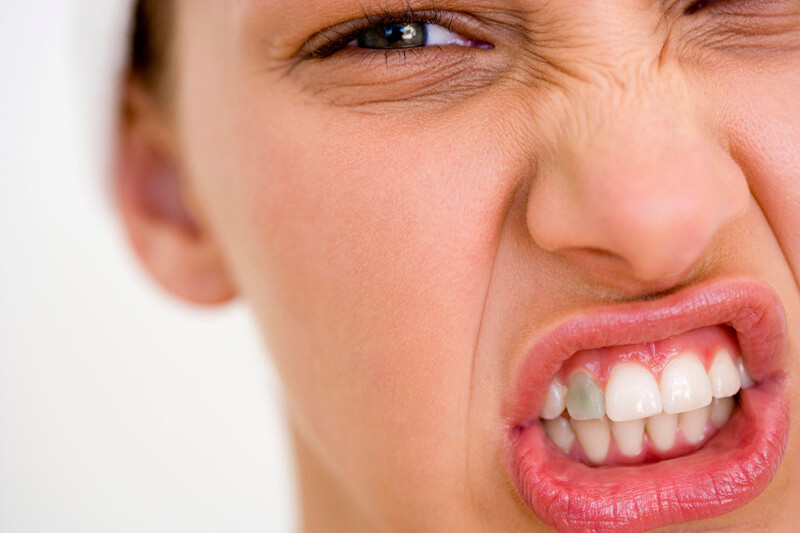

Tartar is bacterial and mineral plaque, forming a thick film on the tooth and surrounding it. Tartar formation begins with a buildup of soft plaque. Routine tooth brushing helps wash it away from the visible tooth surface, but it still deposits and hardens in the interdental spaces or gums.
One way or another, plaque accumulates, causing the gingival margin to sag toward the apical part of the tooth and expose the neck. Given that the enamel thickness in this area is small, the risk of tooth decay increases.
The Clinic of Aesthetic Dentistry offers tartar and deposit buildup removal. Our experts use only cutting-edge technologies: ultrasonic scaler, Air Flow system. In addition, professional teeth cleaning 1-2 times a year can deal with tartar.
Fluorosis
Fluorosis can be another cause of tooth darkening. The disease is caused by the accumulation of excess fluoride in the body during the tooth formation process.
Causes of Teeth Darkening in Children
Baby teeth are affected by decay and turn black much more often than permanent ones. That is why scheduling regular dental checkups for children is recommended. Baby incisors are less dense and respond quickly to any pathological changes in the mouth. Common causes of dental caries in children are considered to be:
- calcium deficiency of various nature;
- poor oral care;
- avitaminosis;
- frequent colds and infectious diseases weakened immune system;
- immunodeficiencies of a more complex nature;
- feeding at night;
- uncontrolled consumption of sugary foods;
- certain diseases of organs and body systems.
Cervical Caries Symptoms
In addition to tooth darkening in the neck area, patients may complain about the following: intermittent pain, increased sensitivity, low aesthetics perception of the smile, and bad breath. This is because cervical caries goes through several stages of development:
- Chalk spot formation. The tooth in the affected area loses its shine and becomes rough. A chalky or pigmented stain is visible if the decay covers the frontal teeth from the outer surface of the teeth.
- Stage of enamel erosion and superficial caries. The stain becomes a defect with progressive deepening and destruction of tissues. Intermittent temperature or food sensitivity occurs.
- The carious process deepens. In moderate caries, the depth of destruction does not reach the pulp; the nervous system can be treated at this stage. On the other hand, deep caries requires pulp removal and cleaning of the root canals from the nerve bundle, as the pulp is involved in the pathological process causing pulpitis.
Most often, the carious process is localized in the lingual tooth surface. However, sometimes it develops circularly and literally damages the entire circumference of the tooth.
Tooth Blackened from the Inside: Disease Diagnoses
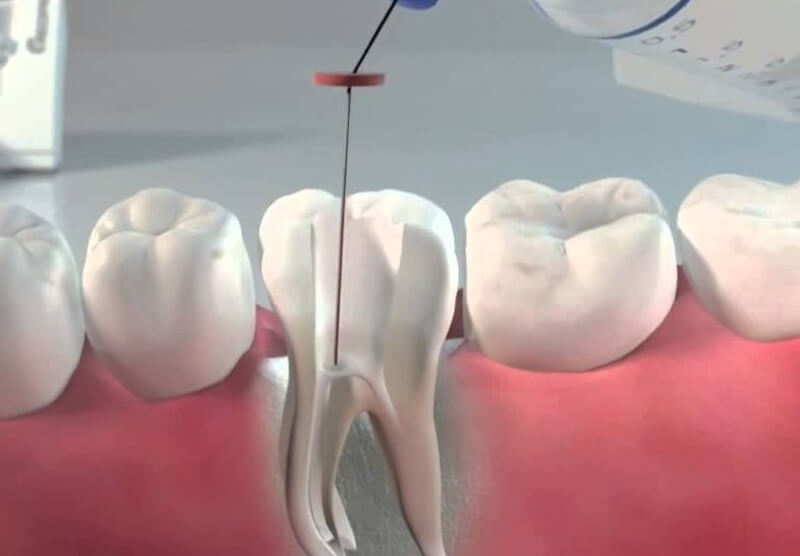
The diagnosis of cervical caries rarely leaves any doubt. A visual examination and instrumental investigation conducted by a dentist is usually sufficient to make a particular diagnosis. In doubtful cases or to clarify the depth of the lesion, the following options are used:
- microscope;
- periapical radiography;
- transillumination.
Differential diagnosis involves excluding diseases similar in visual signs: fluorosis, wedge-shaped defects and enamel erosion.
Front Tooth Filling Turned Black: Treatment
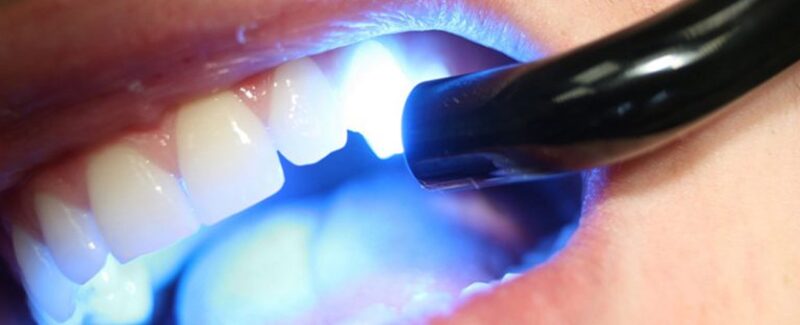
Treatment of cervical caries lesions:
- conservative, by preparation and subsequent filling;
- removal of plaque and tartar with instruments, and good oral hygiene practices as a preventive measure;
- oral cavity debridement to remove the infection;
- remineralization therapy.
There are various protocols for darkened teeth treatment followed by a dental filling. The basic algorithm for conservative treatment of cervical caries is:
- anaesthesia;
- cavity preparation within the defect area;
- filling with light-curing material;
- finishing and polishing – treatment completion.


