What are the best types of dental implants?

Contents:
There are several types of prosthetic solutions. Implant dentures differ in modifications, characteristics, conditions of use, and how dental implants are placed. Only a doctor can choose the best option for a particular case.
The key criteria for classifying dental implants are as follows.
- Design
Implants can be:
| Prefabricated (two-piece) | Monolithic (one-piece) | |
| Structure | They consist of a metal screw and a separate abutment (connector) with the crown fixed | The abutment and the implant are a one-piece monolithic structure |
| Application | They are used in two-stage classical implant surgery | They are placed with the denture as part of the immediate loading implant procedure |
| Placement method | The titanium screw is implanted into the jaw. An abutment is placed on the implant after it has fused into the jaw. A crown, bridge, or plate is placed on the implant | The implant is immersed in the jaw’s bone up to the tip’s level An artificial tooth is fixed on top |
| Advantages | If necessary, the abutment can be changed without removing the implant itself | The simultaneous placement of the implant and denture makes it possible to close the defect of the missing tooth at once |
- Types of implants
- Intramucosal
Intramucosal implants are anchored in the gingival mucosa, provided that it is at least 2 mm thick. They are designed for the fixation of removable prostheses. The base of the prosthetic structure is equipped with a matrix that is connected to the implant by a type of button lock. The gums must be healthy for this type of design.
- Subperiosteal
They are implanted between the periosteum and the jaw bone. They have a particular lattice-like frame that covers the bone mass. In this design, the abutments come out through the gingiva. The design is suitable for denture retention without prior osteoplasty in cases of bone atrophy.
- Mini implants
They are designed for anchoring removable dentures. They are implanted into the jawbone through the gingiva. Due to their small size (1.8 to 3 mm), insertion is quick and virtually painless.
The miniature rods are implanted within 2 to 4 weeks after implant surgery, and the prosthetic structure can be placed 1 to 3 days later. This option suits patients with insufficient bone volume and basal or conventional implantation obstacles.
- Classic
It consists of two parts – an artificial root and an abutment. They are implanted into the bone, provided the bone mass is enough. In case of bone deficiency, osteoplasty is performed several months before or during dental implantation. This is the most popular option. Due to the variety of offers, specialists can choose the right implant for each patient.
- Basal
Such implants have a monolithic design and smaller diameter but are longer than the classic models. They are placed in the basal layer of the jawbone. It is denser, highly resistant to inflammation and resorption processes. Implant surgery is performed using minimally invasive techniques.
- Zygomatic
Dental specialists started using this type of implant relatively recently. The artificial root is implanted in the zygomatic bone. The length of the implants is about 25 mm so that they can be placed without osteoplasty.
- Form
Implants are classified by appearance into:
| Root-form implant | Blade implant | |
| Design | It looks like self-tapping screws. The thread structure can be different | It has a flat shape; it is a narrow, prolonged device with holes in which the bone tissue adheres. Due to these features, no bed preparation bed is required |
| Application | It is placed using both delayed and immediate loading protocols | It is used in case of contraindications to root implants. One design allows two teeth to be restored at once |
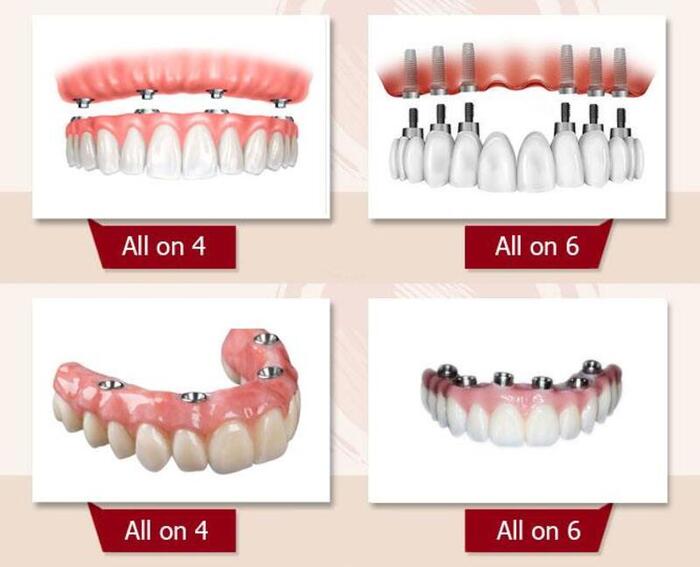
What Are Dental Implants Made of?
The material is metal. To be used in production, it must necessarily meet specific requirements:
- it must be strong enough to withstand the stresses of years of use;
- not destroy the jawbone with its weight;
- retain its original shape until the end of its service life;
- be resistant to the effects of the biological environment;
- not interact with other metal structures in the patient’s mouth (regarding galvanic currents);
- be non-toxic, hypoallergenic;
- have no carcinogenic effects.
These criteria are met by:
- Titanium alloys
The main advantage of titanium is biocompatibility. The metal does not cause an allergic reaction, is very resistant, and not heavy. Grade 4 – titanium (99%) + iron (0.5%) and Grade 5 – titanium (88%) + aluminum (up to 6.75%) + vanadium (up to 4.5%) are used for implants. These materials are used to create products of the leading brands: Straumann, Nobel Biocare, Osstem, and others.
- Zirconium dioxide
It has a white color resembling dental porcelain. Super strong, it is used to create implants, abutments, and crowns. Due to its aesthetic appearance, it is ideal for restoring anterior teeth. Zirconium dioxide is biocompatible, does not cause allergic reactions, and is durable. It is used by CAMLOG and Straumann (PURE ceramic implants).
- Roxolid
A compound of zirconium dioxide (15%) and titanium (85%). Straumann’s idea. The combination of the two materials has resulted in excellent strength properties. Even small-sized products can bear significant loads for many years.
- Tantalum
Two and a half times stronger than titanium. It is also bioinert, not harmful to the body. However, it is used much less frequently due to insufficient prevalence worldwide. Zimmer-Biomet from the USA makes tantalum implants. The range does not include the classics but so-called trabecular models. During their manufacture, small cells resembling trabeculae of natural bone substance are formed on the surface of the products. This property contributes to better osseointegration. Once the implant is placed, the bone grows into the holes, firmly holding the structure.
Other metals – cobalt alloys with chromium, medical steel, gold, nickel are not used for implant production. They are used to creating abutments and elements of prostheses.
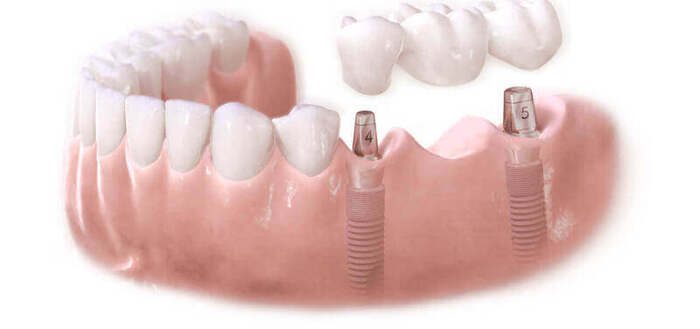
What metal is considered the best?
To choose the best material, you should not be guided only by the properties of the metal. Other criteria include availability, price, and the possibility of application in a particular clinical situation. Titanium alloys meet the above criteria. Numerous scientific studies and 60 years of observational experience make this material optimal for today.
Despite the high strength and other advantages, the significant disadvantage of zirconium dioxide and tantalum structures is their high cost, which means that they are not available for all patients.
How Long Do Implants Last?
In practice, it has been confirmed that titanium prostheses can last at least forty years without complaints, although this period is unlimited. Zirconium implants last for at least thirty years. Tantalum, as well as titanium alloys, should last for life.
How do you choose the “right” implants?
Material properties are an essential consideration when restoring teeth. However, products made of the same metal from different manufacturers or the same manufacturer’s lines are dissimilar. How can you choose the best option? Success depends on several details:
- select a standard factory-made implant; customized designs from dental labs have a short lifespan;
- the best implant shapes are root-shaped and cylindrical, as they mimic the look of natural roots;
- screw threads can be pointed (self-tapping); compression – when the implant is inserted, it seals the jawbone around the bed;
- the surface of the product is made polished or rough; for better osseointegration, it is worth choosing models that are coated with active substances to stimulate the renegration of the jaw bone (phosphorus, calcium, etc.);
- pay attention to the purity of the alloy – the best implants undergo a multi-stage processing to eliminate impurities;
- the model should be suitable for your clinical case – the doctor will ask you to take tests and undergo a dental computer tomography; if there are signs of inflammation or bone loss, the dentist will recommend an option considering the indications.
The most important thing is to find an experienced and responsible doctor, as the result of implantation or prosthetics depends on the professionalism and integrity of the specialist.
At KES Clinic, you can easily solve the problem with dentures. Our doctors will select the best implant option for you. Contact us!

