Sedation in Dentistry – Types of Sedation in Dentistry

Contents:
Sedation in dentistry is a modern and comfortable method of dental treatment. The essence of the procedure is a temporary blocking with anaesthetic drugs of brain areas responsible for an increased level of anxiety.
In a state of sedation, a person calms down and plunges into a superficial sleep while remaining conscious. Despite the increased popularity of the procedure, patients often have questions about its contraindications, sedation risks and whether children can have it.
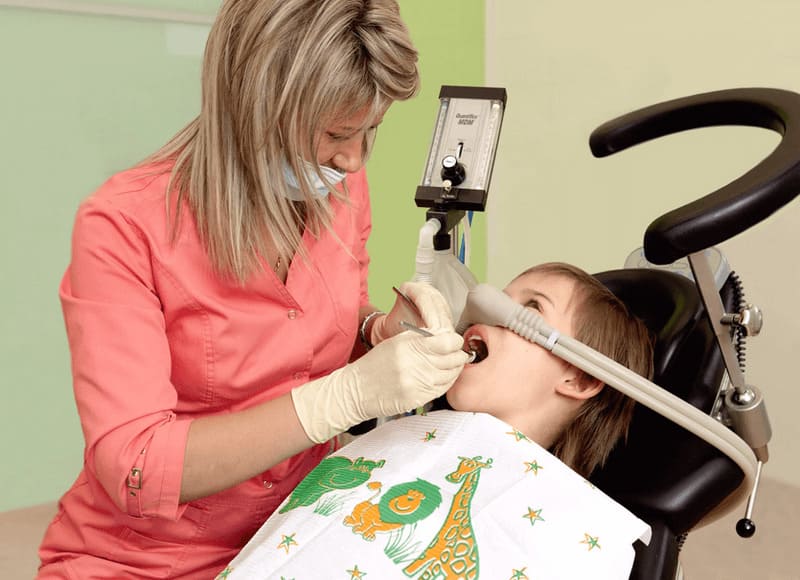
What Is Sedation in Dentistry?
This state is similar to sleep. The person is conscious but simultaneously wholly relaxed physically and emotionally. The patient can communicate with the doctor, respond to stimuli, breathe spontaneously, and have normal reflexes. A sedative is French for soothing.
Sedation in dentistry helps to relax and administer local anaesthesia painlessly and without fear.
There are three stages of sedation in dentistry:
- Light. The patient is relaxed but awake and in contact with the doctor. Reactions and coordination are slightly reduced. This is anxiolysis.
- Moderate. The patient responds to tactile stimuli, and all functions and reflexes are within normal limits.
- Deep. Reactions are observed only to strong stimulation. The patient does not respond to sound stimuli. The cardiovascular system operates normally, but breathing may be irregular.
The main advantages of sedation include the following: it does not cause addiction, has practically no contraindications or age restrictions and quickly relieves fear.
Sedation is the ability to remove the gag reflex, increase pain tolerance, and increase the efficiency of local anaesthesia.
To reduce the risk of developing negative consequences, you must first undergo an examination. Be sure to do clinical and blood chemistry tests, tests for HIV and hepatitis, and ECG. If you have a pre-existing chronic illness, get a checkup from your doctor. All patients require consultation with an anesthesiologist.
Indications and Contraindications for Sedation
Sedation is a good option for patients who fear or panic and have high blood pressure due to stress while visiting a dentist. The technique is helpful for people with an increased gag reflex and a reduced pain threshold. Apply if long-term treatment is required, requiring one visit to the doctor.

Sedative drugs are used for various dental procedures.
Light sedation is used for:
- simple operations on the gums;
- cavities treatment;
- pulp and teeth extraction;
- professional dental cleaning;
- periodontal pocket cleaning;
- preparing for prosthetics.
Indications for deep sedation:
- open sinus lift surgery;
- flap surgery within the periodontal disease treatment;
- complex periodontal surgeries;
- correction of severe malocclusion types;
- some mental disorders.
Contraindications for sedation:
- less than three years old;
- allergic reaction and intolerance to sedative drugs components;
- arterial hypertension, cardiovascular disease, pregnancy.
In case of inhaled intranasal therapy – runny nose, nasal congestion.
The procedure is not applied in case of epilepsy – after using sedative gas, intracranial pressure may increase, provoking an attack.
Sedation should be avoided in case of tuberculosis, hepatitis, myasthenia gravis, mental disorders, and alcohol and drug addictions.
Dental treatment with sedation
In dentistry, there are several methods of administering anti-anxiety drugs. Each method has advantages and disadvantages.
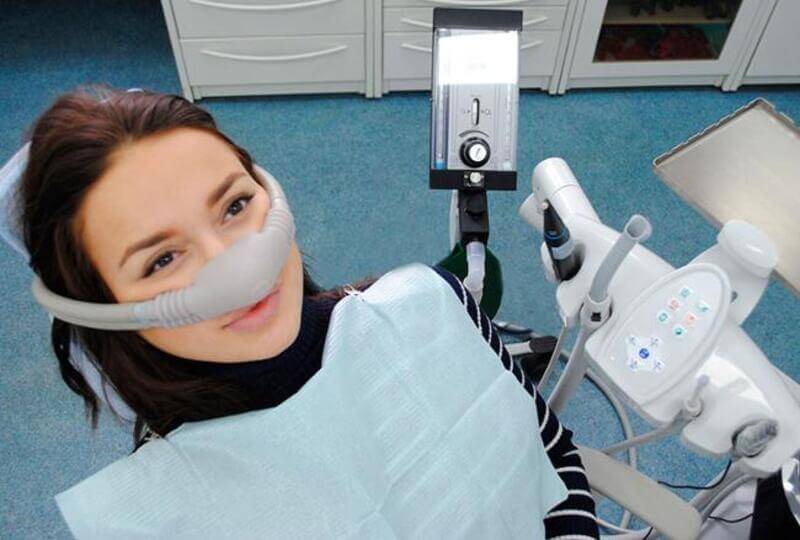
| Method | Description | Disadvantages |
| Inhalation | A simple and safe method, the drug absorbs quickly; a doctor can easily control the process. After the manipulations, consciousness is quickly restored. Most often, nitrous oxide is used – it relaxes well, inhibits motor activity, and has a slight analgesic effect. | ● High cost. ● Staff who can carry out life-saving measures is required. ● Requires special equipment. ● Do not use if the person has problems with nose breathing. |
| Intramuscular or intravenous sedation is an injection of the drug | A patient gets a drug through an injection or a drip. Sedative drugs are used, but the patient’s basic reflexes and breathing are not impaired. | ● It is impossible to increase the medicine’s effect if necessary. ● Long-term effect on the body. |
| Oral | If a person is afraid of needles, pills can be an option. Unable to maintain concentration at the desired level. | ● It affects slowly. ● The drug effect lasts 3-4 hours. ● It is impossible to maintain concentration at the desired level. ● Help only to relieve the patient of fear |
| Intranasal administration | The anaesthetic is administrated into the nasal passages; it quickly enters the brain tissue through the taste buds. Sprays are becoming increasingly popular due to the drug’s ease of use and high bioavailability. | It is impossible to strengthen the action and control the patient’s condition. |
Is sedation harmful to children? According to statistics, every second child hides their dental problems precisely because of the fear of the dentist, leading to dangerous complications.
Many doctors believe this treatment method is justified if others do not work, but it is necessary to follow the rules and select the dosage of drugs strictly. Most often, nitrous oxide is used to treat children’s teeth under sedation.
Dental Treatment under Anaesthesia
What is the difference between sedation and anaesthesia? Anaesthesia dramatically increases the degree of inhibition, switches off consciousness, and suppresses the reflexes; the patient does not respond to stimuli. The anaesthesia function is to immerse a person in a state where you feel nothing.
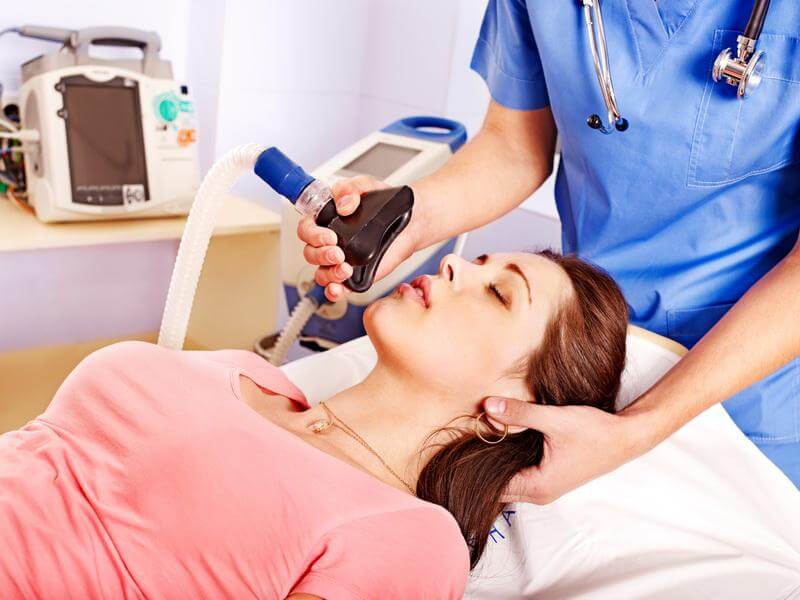
Some medical terms in ordinary life acquire additional meanings. In 99% of cases, the phrase “to treat teeth under anaesthesia” means the use of sedatives. Due to this common mistake, even dentists use the term “anaesthesia” when they mean the use of drugs to depress consciousness while maintaining reflexes and consciousness.
General anaesthesia in dentistry is rarely used, mainly in the maxillofacial surgery department. Manipulations require special equipment to control heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, and oxygen levels.
Treatment under sedation, when compared with anaesthesia, is a safer and more straightforward procedure; it has fewer contraindications and side effects.
Sedation – side effects
The adverse effects of sedation depend on the administration route and the drug effect mechanism. In the beginning, some patients experience increased activity and sociability. An obsessive cough attack sometimes begins; in such cases, the drug dosage is adjusted.
Sedation – possible side effects:
- very rarely – temporary loss of consciousness immediately after treatment;
- rarely – a feeling of euphoria, headache, dizziness, chills, irregular heartbeat, cough, nausea and vomiting, fever;
- often – pain at the injection site with intravenous medication.
Does sedation have dangerous side effects? No, the procedure is completely safe for adults and children over three years of age when performed by an experienced physician. The specialist must undergo special training; the clinic must have all the necessary equipment to eliminate emergency consequences.
However, sedation is not a magic pill for all occasions; it will not replace painkillers. This state allows the patient to relax, get rid of fear, and calmly endure all further manipulations of the dentist.

