Crossbite: Types, Signs, Causes, Treatment, and Prevention

Contents:
According to statistics, 9 out of 10 people have a crossbite. It comes out differently: the front teeth protrude forward, the tooth rows are partially or entirely misaligned, the lower jaw is moved backwards, etc. About 2-3% of the population suffers from crossbite, a condition where one or more teeth of the lower row overlap the upper row, and the tooth rows cross over each other. Below, you will find out how to correct uneven teeth and get an aesthetically pleasing healthy smile at the KES Clinics.
Types of Crossbite – the Anomaly Classification and Symptoms
According to the anatomical features, there are 3 types of crossbite:
- Buccal. Occurs with a narrow or underdeveloped upper jaw, resulting in a wider lower row of teeth overlapping some teeth in the upper row.
- Lingual. Occurs in the opposite situation – a reduction in the size of the lower row of teeth and/or jawbone.
- Mixed. Combines the symptoms of both anomalies and is considered the most difficult to correct.
Each option can be unilateral or bilateral. Crossbite also includes cases when only one lower tooth overlaps the corresponding upper tooth. This option is considered to be the most favourable and easy to correct.
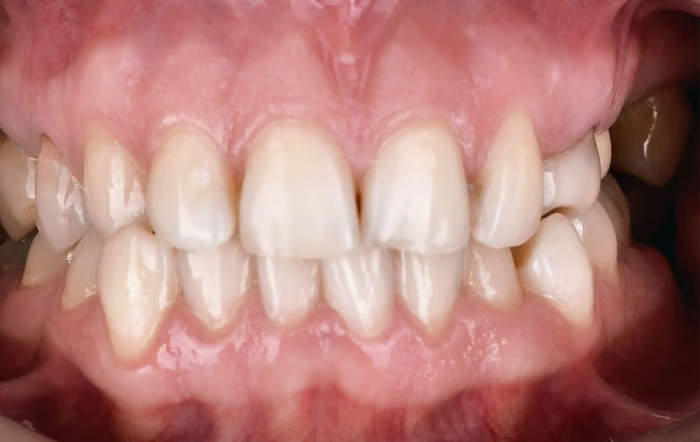
The main symptom of the anomaly is a visible crossing of several teeth, which causes aesthetic discomfort and creates difficulties in chewing food. Sometimes, the pathology is accompanied by a significant change in the size and structure of the jaw; there is facial asymmetry, deviation of the chin to the side, and depression of one of the cheeks. There may be articulation problems, tongue biting and oral mucosa.
Crossbite causes
Pathology at the intrauterine stage of jaw development, and the formation of dental rudiments can cause congenital forms of anomaly. Such pathologies are caused by aggravated heredity and various genetic syndromes.
Acquired crossbite occurs under the influence of multiple causes:
- failure of the timing and sequence of the loss of deciduous teeth;
- ENT diseases (adenoiditis, chronic rhinitis, maxillary sinusitis), which cause nasal congestion and the habit of mouth breathing;
- bad habits in childhood: sucking a finger, biting the lip;
- increased tooth abrasion;
- loss of teeth as a result of tooth decay or periodontitis;
- facial trauma;
- temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ);
- deformities of the cervical spine.
Stages of Crossbite Development
The anomaly’s development stages depend on its cause. The dentoalveolar option of the pathology begins with abnormal eruption, displacement, or loss of teeth. At the same time, the jaws have a physiological position and size. The pathology does not develop further if the condition is noticed and corrected in time. Otherwise, the anomaly develops according to the skeletal type, in which the jaw configuration is disturbed, and facial asymmetries occur.
Skeletal crossbite can be an independent form of pathology. It is characteristic of congenital underdevelopment of the jawbone or violation of its structure due to trauma or surgery.
Crossbite Diagnosis
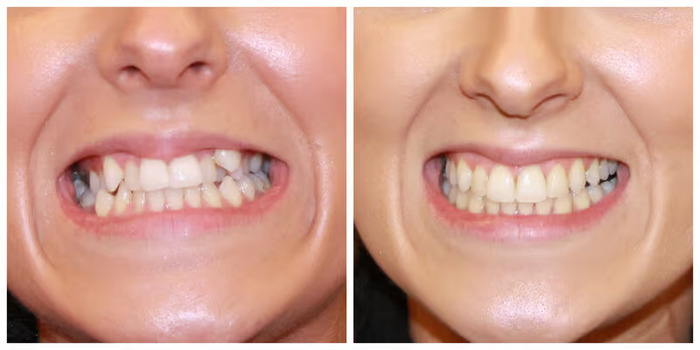
Diagnosis begins with a consultation with an orthodontist and an oral examination. In case of concomitant TMJ problems and masticatory disorders, it is recommended to visit a gnathologist.
To determine the type of anomaly, instrumental examinations are performed:
- orthopantomogram – a panoramic image that shows the entire tooth row and surrounding tissues;
- CT scan of the jaw – a high-precision method that allows for 3D reconstruction and a comprehensive assessment of the dento-alveolar system.
Implications of Having a Crossbite
For many patients, the aesthetic imperfection of the smile plays a decisive role, especially if the crossbite affects the incisors and canines. A person feels embarrassed to communicate with people, avoids being noticed in public, does not smile in photos, and feels self-conscious when building relationships with the opposite sex.
Crossbite negatively affects the health of the dentoalveolar system, causing complications such as
- chipping of enamel and increased unilateral tooth erosion;
- rapid plaque formation due to difficulty in brushing teeth;
- high risk of tooth decay and periodontitis;
- premature tooth loss;
- pain during chewing and speaking caused by muscle strain, secondary TMJ pathology;
- speech defects, which are especially noticeable in congenital pathology.
Crossbite Correction
Given the number and severity of consequences for the dentoalveolar system, crossbite should be corrected as early as possible. After treatment, the patient gets an aesthetically pleasing smile and eliminates problems and discomfort while chewing food.
Bite Correction in Children
In children, the jaw bones and tooth roots are more pliable, so all orthodontic treatments are much easier. If the crossbite is caused by an incorrect change or curvature of individual teeth, orthodontic methods are indicated: plates, bracket systems, and children’s aligners. Working with a speech therapist and psychologist may be necessary to correct speech disorders and eliminate bad habits.
In case of significant narrowing of the upper jaw, a more complex treatment using palatal expanders is prescribed. They increase the width and area of the palatal space and create space for the correct positioning of permanent teeth.
Bite Correction in Adults
Treatment is possible at any age. Doctors use 2 main methods:
- Orthodontic treatment with braces or transparent mouthguards – aligners. Correction of the anomaly takes about 2 years; in some cases, it will take up to 3 years.
- Orthognathic surgery – surgery to correctly align the jaws. Surgical intervention is prescribed in complex cases before orthodontic correction.
For treatment to be successful and comprehensive, the cause of the bite abnormality should be eliminated if possible. In the case of TMJ pathology, a joint splint is prescribed, and exercises for the masticatory muscles. To eliminate dental defects, prosthetics, or implantation is performed.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is necessary to correct the jaw’s shape and size in the skeletal anomaly. The main technique is osteotomy of the upper or lower jaw. To correct facial asymmetry and chin curvature, a dentist can suggest genioplasty. The doctor selects the surgery tactics individually based on the examination results.
Bite Correction with Braces
Braces are the most common and effective way to correct crossbites. Metal appliances allow one to position the teeth in the row correctly, to achieve physiological jaw alignment, and to correct crossbites of individual teeth.
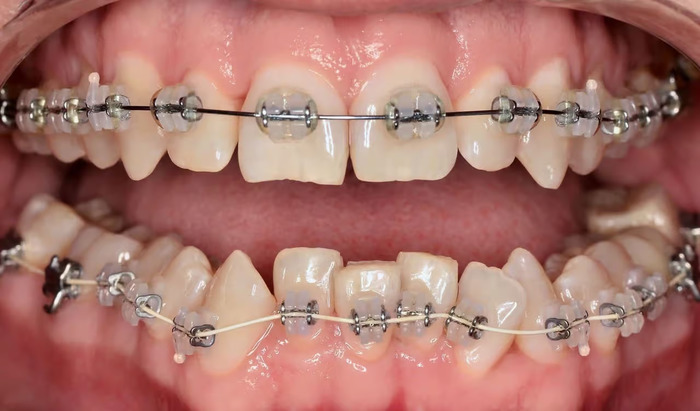
Braces are used to correct permanent teeth. They are used in adolescents after a bite change and in adults without age restrictions. To consolidate the achieved effect after treatment, retainers are placed; they are invisible when smiling and comfortable to wear.
Possible Problems of Crossbite Treatment
The orthodontist’s primary goal is to restore the normal position of the jaw and align the teeth. However, during treatment, a person may experience pain in the temporal area, chewing problems due to the gradual displacement of teeth and other complications.
The doctor takes a comprehensive approach to therapy and selects an individual programme that includes additional methods:
- special gymnastics;
- taking painkillers;
- dietary correction.
Prevention of Crossbite Anomalies
There are no preventive measures if congenital anomalies of the dentoalveolar system cause crossbite. The main task is to pay attention to the abnormal position of the child’s teeth in time and bring them to an orthodontist to choose treatment.
To reduce the risk of cross anomalies throughout life, it is necessary to:
- follow your daily oral hygiene routines;
- visit a doctor in time for tooth decay treatment;
- go for a check-up every six months;
- have your mouth professionally cleaned every six months.
Treating nasal breathing pathologies on time and eliminating bad habits is important.

