Sinus lift as a method of bone augmentation
Contents:
A sinus lift is an operation in maxillofacial surgery, which increases bone tissue volume. A sinus lift is required for implantation of the teeth of the upper jaw. The surgery allows achieving a solid base for the future implant with a length of more than 10 mm by increasing the jawbone’s thickness and height.
Bone mass is increased by filling an artificially created cavity in the maxillary sinuses.
Indications for Maxillofacial Surgery
The purpose of bone augmentation is to elevate the maxillary sinus floor and fill the formed cavity with osteoplastic material. Thus, the bone mass is replenished, creating a solid foundation for subsequent implant screwing. A sinus lift is required for patients with atrophic upper jawbone tissue.
Key indications:
- the volume of the bone tissue of the tooth between the dental curve and the maxillary sinuses is less than 8 mm;
- displacement of the paired sinuses closer to the oral cavity;
- deep alveolar opening;
- significant atrophic changes.
85% of patients with prolonged tooth absence require a sinus lift.
Types of Sinus Lift
There are three fundamental methods of sinus lift that doctors around the world practice. The specialists of the Clinic of Aesthetic Dentistry in Kyiv have vast experience in facial surgery; they will select the most suitable method for bone augmentation. The method’s choice depends on the nature of atrophic processes, the initial height of the alveolar ridge, the patient’s age, and other general clinical aspects.
Open or Lateral Sinus Lift
Open sinus lift involves performing a complex maxillofacial surgical procedure. The method allows increasing the height of the bone mass up to 8 mm. Thus, open sinus lift is suitable for patients with significant bone atrophy.
The procedure is performed according to the following algorithm:
- incision of the mucosa and detachment of the gingival flap;
- drilling a window;
- placement of bone grafting material;
- wound closure.
The rehabilitation process is long, and it takes at least six months. The main disadvantage of the method is the risk of maxillary sinus perforation. That is why a doctor with colossal experience in the field of maxillofacial surgery should conduct the surgery.
Closed Sinus Lift
A closed sinus lift is a low-traumatic method of increasing the maxillary bone volume in the intended implantation area. The procedure is advisable if the initial height of the dental curve is at least 6 mm.
Technique:
- drilling a window with a medical drill;
- probing and delivery of bone grafting material into the cavity between the dental curve and the sinus floor;
- installation of an implant;
- gingival suture if necessary.
One-stage implantation is performed for the closed sinus lift. There is no point in waiting for the wound to heal: the hole has already been formed, and the gums’ mucous membranes do not need long-term recovery. At the request of the patient, implantation can be performed later. A closed sinus lift is justified if installing no more than two implants within the maxillary sinuses.
Balloon Sinus Floor Elevation
The balloon sinus lift technique is recommended for a bone height of 3-4.5 mm. The main advantage is the ability to carry out bone augmentation along with implantation. The procedure’s principle is similar to the closed sinus lift technique; a balloon is used instead of bone grafting material. It is introduced through a special opening with a probe, injected with air, and left there for natural exfoliation of mucous membranes and filling the cavity with connective and bone tissue.
The whole procedure takes about an hour. Methods involve local anesthesia, but sometimes general anesthesia or additional sedation is required. It is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination to understand the hazard.
Preparation
Preparation for a sinus lift includes examining the oral cavity, assessing the teeth’ condition and mucous membranes. Based on the analysis results, a computer-aided tomography of the jawbones, an X-ray of the paranasal sinuses is recommended. These studies allow the specialists to understand the height of the alveolar tissue, the density, and the jawbones’ volume in the area of implantation.
The doctor examines the patient’s clinical and medical case history. In case of doubt, blood and urine tests are required. With a complicated medical history, it is essential to enlist particular specialists’ advice: cardiologists, nephrologists, neuropathologists, etc.
Contraindications
The absolute contradictions to sinus lift are similar to contraindications to any other surgical operation and cover the following aspects:
- neoplasms, polyps, oncological diseases;
- immunodeficiencies of various origin;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- psycho-neurological disorders, drug and alcohol addiction;
- heart diseases;
- organ failure;
- critical allergic reactions to drugs (anesthesia).
A sinus lift is not carried out with acute exacerbation of chronic sinusitis and other types of sinusitis, anomalies in the development, shape, or size of the maxillary sinuses, previously performed paranasal sinuses surgery, and maxillary osteomyelitis. A sinus lift is not repeated if there have been previous cases of implant failure.
Time Limits for Denture Treatment
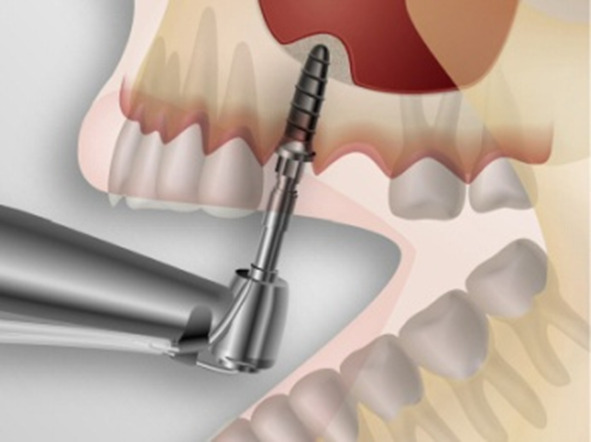
In terms of closed and balloon sinus lift, implantation with immediate loading can be performed. In this case, immediately after the bone augmentation, an implant is screwed in, holding a temporary prosthesis. After osseointegration and osteoplastic material engraftment, a permanent prosthesis is installed. The implant is inserted 3-6 months after the tissues have completely healed with an open sinus lift.
Possible complications
Complications of sinus lift performed by a highly-qualified doctor are rare today, and the surgery success leaves no doubt. Despite this, the risks still exist:
- Mechanical damage. A common complication is the rapture of the Schneiderian membrane – the floor of the maxillary sinuses. If the injury’s diameter does not exceed 2 mm, then the wound heals on its own, provided that the implant is firmly fixed. With significant tissue damage, compulsory treatment is required. Sometimes you have to give up dental implantation.
- Infection. Inflammation occurs with insufficient oral hygiene or violations of antiseptic rules during manipulation. Sometimes the condition is triggered by an acute exacerbation of sinusitis, for example, during or immediately after surgery. Inadequate treatment or insufficient control over the situation leads to bleeding, fistulas, generalized inflammation, and abscess.
- Mobility of the implant or osteoplastic material. Both jaw trauma causes implant mobility after surgery or a violation of the technique for sinus lift performing. The mobility of the implant or implanted bone component requires a new surgery.
In the early postoperative period, bleeding of the gums, slight swelling, pain in the exposed area, fever, dizziness, and weakness are considered normal. These symptoms disappear within a few days after surgery.
Recovery period
After the surgery, it is necessary to abstain from eating for 1-2 hours. Within the first week, it is important to limit yourself to a menu with liquid or semi-liquid food and plenty of drinking. Hard, coarse food, spices, sour, and salty dishes should be excluded from the diet. You can not drink alcohol or smoke. Tobacco smoke provokes vasospasm and can disrupt the process of tissue engraftment, osseointegration.
Next month, it is essential to keep a protective regimen to avoid long flights, hot saunas, baths, and physical exercise. Besides, it is necessary to observe preventive measures for respiratory infections that can lead to an acute exacerbation of the chronic disease, for example, sinusitis: wear masks, avoid crowded places, especially during periods of high epidemiological risks. The oral cavity is regularly rinsed with an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, Nitrofurazone, Miramistin.

